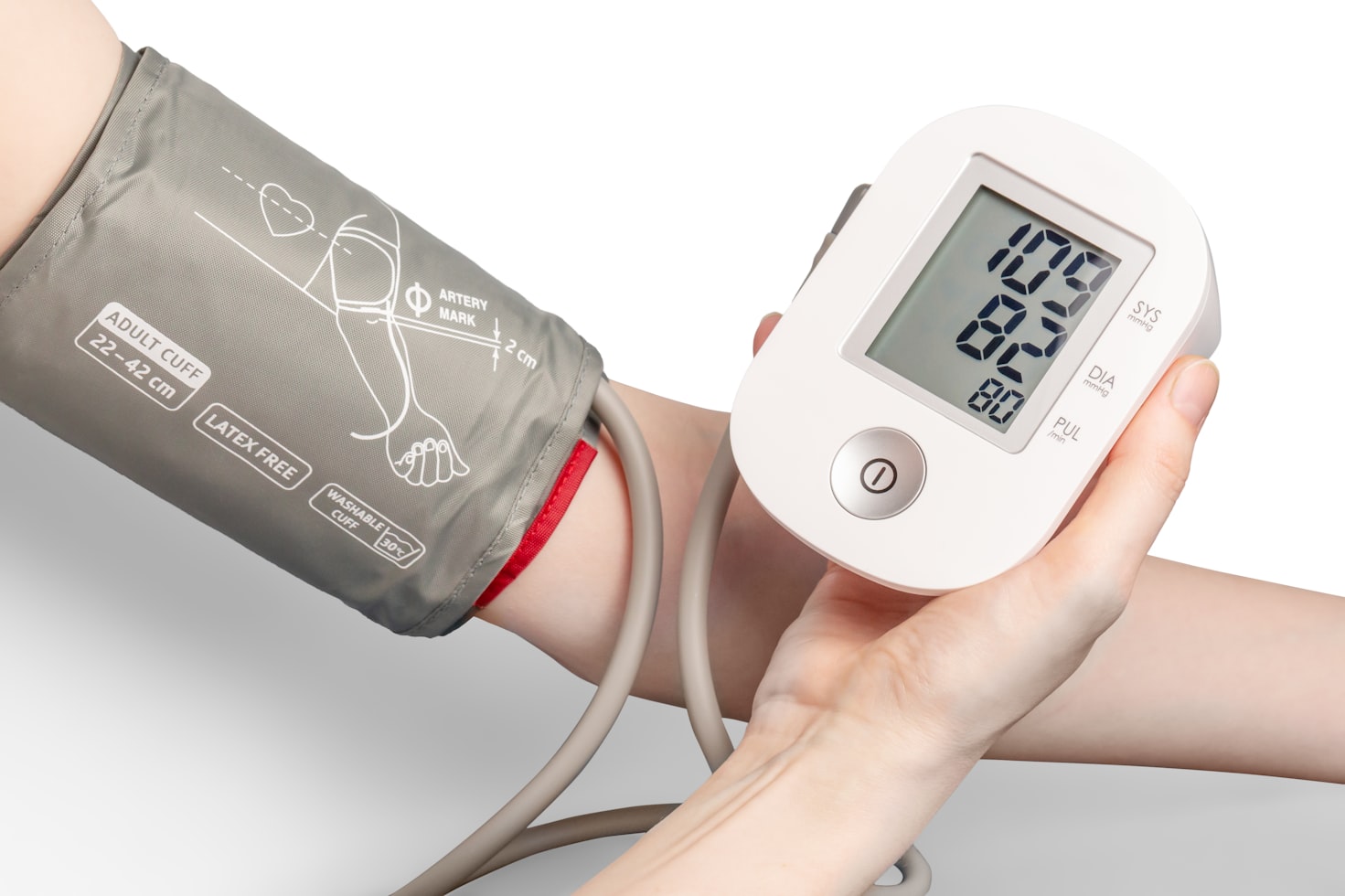
Monitoring your diastolic blood pressure at home is an essential way to take control of your health and prevent serious medical conditions like heart disease, stroke, or kidney failure. It’s an easy, cost-effective, and convenient way to track your blood pressure regularly, which helps you identify any potential health risks early on. But how can you effectively monitor your diastolic blood pressure at home? In this article, we’ll provide you with helpful tips and tools to accurately measure your diastolic blood pressure, interpret the readings, and take action if needed. From understanding the importance of blood pressure monitoring to choosing the right monitoring device, we’ve got you covered!
Blood pressure is a critical indicator of human health. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to various heart diseases and strokes. Monitoring your blood pressure regularly can help you avoid such health risks. Moreover, Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) is the lower reading of a blood pressure measurement, indicating the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest. Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) of a healthy person lies between 60 to 80 mm Hg. In this article, we will discuss how to monitor your Diastolic Blood Pressure at home with various tools and tips.
Blood Pressure Cuffs
The most common method to measure Blood Pressure is by using a Blood Pressure cuff, also known as a sphygmomanometer. A blood pressure cuff is a device that consists of a cuff, gauge, and inflation bulb. You wrap the cuff around the arm, inflate it, and listen to the sound of the pulse with a stethoscope to determine blood pressure. It is essential to calibrate your blood pressure cuff regularly to ensure its accuracy. You can buy a blood pressure cuff from a health store, pharmacy or online store. Manual blood pressure cuffs are standard, but digital blood pressure monitors are also available. However, before purchasing a digital blood pressure monitor, make sure it is accurate and reliable by checking reviews and ratings online.
Wrist Cuffs
Wrist cuffs are an alternative to standard arm cuffs. They measure blood pressure similarly to arm cuffs, but they wrap around the wrist, making them convenient to use. It is essential to use proper techniques with wrist cuffs, such as placing the measuring sensor at heart level, to ensure accuracy. Moreover, people with large or weak wrists may have difficulty using wrist cuffs. It is also worth noting that wrist cuff readings may differ from those taken by arm cuffs. Despite this, if you are unable to use standard cuffs or prefer wrist cuffs, they can be a reasonable option.
Finger Cuffs
Finger cuffs are the most portable method to measure blood pressure. The cuffs wrap around the finger like a ring, and you can take readings from your fingertips. Unlike arm cuffs, finger cuffs do not require stethoscopes to determine blood pressure. Instead, these cuffs have a built-in sensor that measures blood pressure. Finger cuffs are suitable for people who travel frequently, as they are compact and convenient to carry. However, finger cuffs are less accurate than arm cuffs, and they are not recommended for clinical use. In general, they may be a useful tool for getting a general idea of your blood pressure, but they should not replace regular monitoring with an arm cuff.
Tips for Accurate Measurements
Monitoring your Diastolic Blood Pressure accurately requires specific techniques to achieve optimal results. Firstly, it is crucial to find a quiet and comfortable environment for measuring your blood pressure. Stress, anxiety, and physical exertion can affect blood pressure, so it is necessary to relax before taking readings. Secondly, ensure that the cuff’s size is appropriate for your arm or wrist; the cuff’s bladder should cover about two-thirds of the arm’s length. You should also rest for five minutes before measurement, and avoid talking or moving during the test. Lastly, it is essential to keep a record of your readings regularly to monitor improvements or worsening of your blood pressure.
In conclusion, monitoring your diastolic blood pressure at home is essential for maintaining good cardiovascular health. With the right tips and tools, you can obtain accurate readings and track changes in your blood pressure over time. By investing in a quality blood pressure monitor, following the correct measuring techniques, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can better control your blood pressure and reduce your risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. Remember to consult your doctor if you notice any significant fluctuations in your blood pressure readings.